Understanding the method of reproduction in biological organisms is crucial in the study of biology. Whether you’re examining plants, animals, or microorganisms, recognizing the type of reproduction used by an organism can help explain its life cycle, genetic variations, and evolutionary advantages.
In this guide, we will not only help you identify the method of reproduction in the given diagram but also explain the different types of reproduction, their processes, and their significance.
By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of how to analyze biological diagrams and be equipped to identify the reproduction method in various organisms.
Identify the Method of Reproduction in Given Diagram
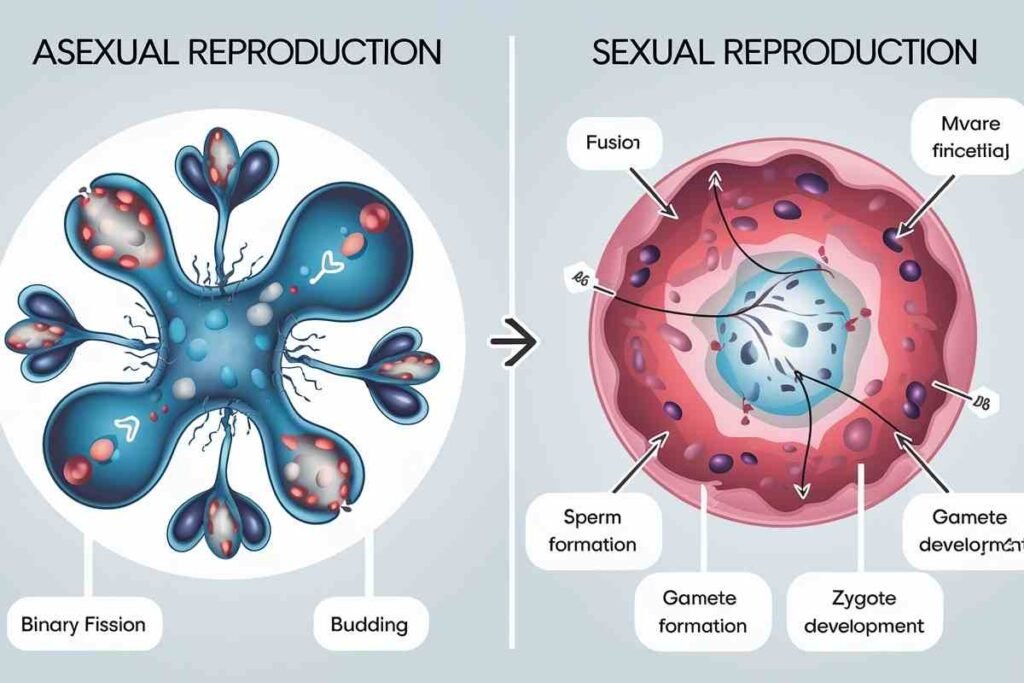
Reproduction is the biological process by which organisms create offspring to ensure the survival of their species. Broadly, reproduction can be classified into two categories:
- Asexual Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction
Both methods are essential for the propagation of species, but they differ in terms of the number of parents involved and the genetic makeup of the offspring.
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction involves a single parent organism. Offspring produced through asexual reproduction are genetically identical to the parent (clones) as there is no involvement of gametes (sperm and egg cells). This method allows organisms to reproduce rapidly and without the need for a mate.
Methods of Asexual Reproduction
| Method | Description | Example Organisms |
|---|---|---|
| Fission | The parent organism splits into two or more identical offspring. | Bacteria, Amoeba |
| Budding | A new organism grows from a bud or outgrowth on the parent, which later detaches. | Hydra, Yeast |
| Fragmentation | The organism breaks into pieces, and each piece forms a new organism. | Planaria, Spirogyra |
| Parthenogenesis | Offspring develop from an unfertilized egg without fertilization. | Aphids, Komodo dragon, some reptiles |
Each of these methods occurs in different organisms and plays a unique role in ensuring survival in stable environments.
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction involves the combination of reproductive cells (gametes) from two parents, typically a male and a female.
This process results in offspring that have genetic material from both parents, leading to genetic diversity. Genetic variation is essential for the adaptation and evolution of species, especially in environments that change over time.
Process of Sexual Reproduction
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Gamete Formation | Specialized cells (sperm and egg) are produced by the parents through meiosis. |
| Fertilization | The sperm and egg cells fuse to create a zygote. |
| Development | The zygote divides and develops into a new organism, inheriting traits from both parents. |
Types of Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction can occur in two primary forms based on where fertilization takes place:
- Internal Fertilization: Common in mammals, birds, and reptiles, where fertilization happens inside the female’s body.
- External Fertilization: Common in aquatic organisms like fish and amphibians, where fertilization occurs outside the female’s body, usually in water.
Common Diagrams You Might Encounter
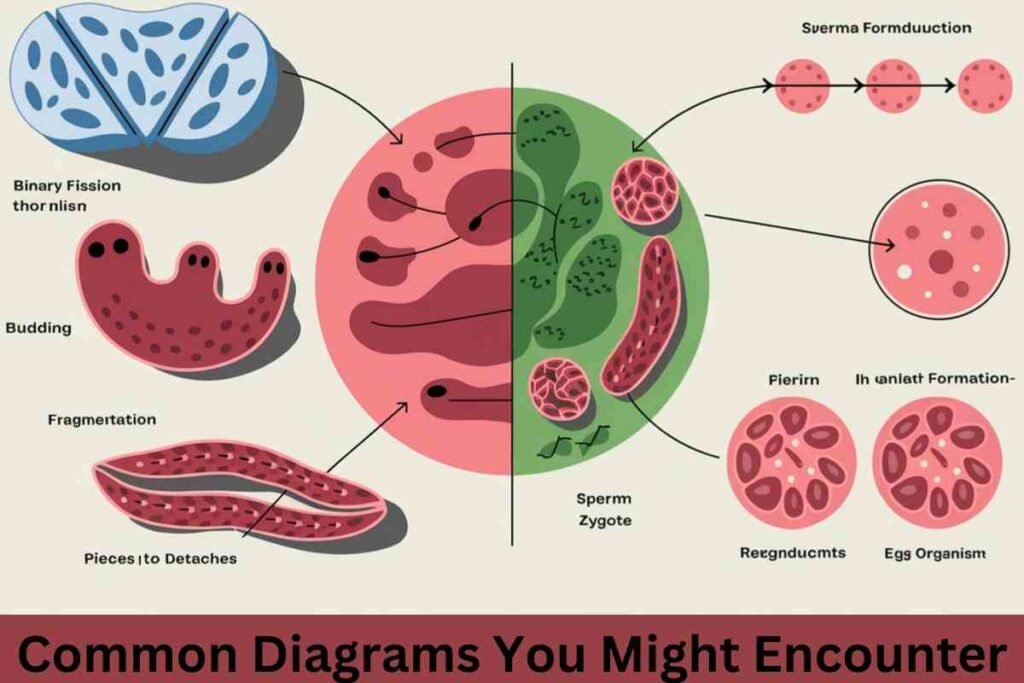
Biological diagrams are often used to represent these methods of reproduction visually. Here are common reproductive processes you might see:
- Binary Fission: A bacterium splitting into two identical daughter cells.
- Budding: A small bud forms on the body of a Hydra, which later detaches to become a new organism.
- Fragmentation: A Planaria is split into pieces, with each piece growing into a new organism.
- Fertilization: A diagram showing sperm and egg cells coming together to form a zygote.
These diagrams provide clear visual representations of the reproductive methods and can help in identifying the reproduction process in various organisms.
Why Understanding the Method of Reproduction Is Important
Genetic Diversity and Survival
In sexual reproduction, genetic variation plays a crucial role in the species’ ability to adapt to changing environments.
By combining genes from two parents, sexual reproduction helps produce genetically diverse offspring, which increases the chances of survival in dynamic conditions.
Rapid Population Growth
Asexual reproduction, on the other hand, allows for rapid population growth. Since offspring are produced without the need for a mate, the process is faster, making it advantageous in stable environments where genetic variation is not as critical.
Human Impact on Reproduction
Humans have learned to manipulate reproduction for agricultural purposes, using techniques like vegetative propagation and grafting to reproduce plants with desirable traits. This has led to the production of crops that are disease-resistant or better suited to specific environments.
Conclusion
Identifying the method of reproduction in a diagram requires a clear understanding of both asexual and sexual reproduction.
Each method, whether binary fission, budding, or fertilization, plays a crucial role in the survival and evolution of species. By mastering these processes, you’ll be able to recognize reproduction methods in various organisms with ease.
This knowledge provides deeper insights into biological life cycles and the mechanisms that drive genetic diversity and species adaptation. Understanding these fundamental concepts is key to grasping the complexity of life.
FAQs
What is asexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction involves a single parent organism producing offspring that are genetically identical to itself. Common methods include fission, budding, and fragmentation.
What is sexual reproduction?
Sexual reproduction requires two parent organisms, typically male and female, whose reproductive cells (gametes) combine during fertilization to create genetically diverse offspring.
How can I identify asexual reproduction in a diagram?
Look for signs of a single parent organism, such as binary fission (splitting), budding (a new organism forming from the parent), or fragmentation (pieces of the parent forming new organisms).
What are the main types of asexual reproduction?
The main types of asexual reproduction include fission, budding, fragmentation, and parthenogenesis. Each method produces offspring without the need for gametes.
What is the difference between binary fission and budding?
Binary fission involves the division of a single organism into two identical offspring, while budding involves the growth of a small outgrowth on the parent, which later detaches to form a new organism.
How do I recognize sexual reproduction in a diagram?
Sexual reproduction is indicated by two parent organisms (usually male and female) and the presence of gametes (sperm and egg cells) merging to form a zygote.
What is parthenogenesis?
Parthenogenesis is a type of asexual reproduction where offspring are produced from an unfertilized egg, common in some insects, reptiles, and amphibians.
Why is sexual reproduction important?
Sexual reproduction introduces genetic variation, which helps organisms adapt to changing environments, promoting survival and evolution.